Hyperlipidemia is an increase in bad cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein (LDL)) or triglycerides (triglycerides) or both in the blood. This can lead to blockage of blood vessels and have serious effects on heart health.
A study from the American Academy of Family Physicians found that 1 in 3 adults in the US has high levels of LDL cholesterol. This is why doctors always recommend that patients cut down on foods high in LDL and increase their consumption of foods high in good cholesterol (HDL). HDL-C is called good cholesterol because of its ability to help transport bad cholesterol out of the body. (first)
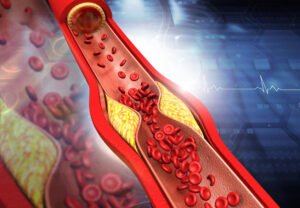
High blood fat is also known with other terms such as hyperlipidemia, hyperlipidemia, dyslipidemia or dyslipidemia.
What are the symptoms of high blood fat?
In rare cases, people with very high cholesterol levels will experience the following symptoms:
Yellow lumps or wrinkles underneath the skin (formed by a buildup of fat around tendons and joints).
There is a white arc around the cornea of the eye.
Lumps in the inner corner of the eye.
This condition can cause serious problems if not detected and treated promptly. Because it causes plaque to build up inside the blood vessels, which can lead to a heart attack or stroke because the blood is partially blocked, essential nutrients and oxygen are not supplied to the brain and heart for these organs to function.
Causes of high blood fat
According to statistics in the United States, there are about 93 million adults (aged 20 years and older) with a blood lipid level higher than the recommended limit of 200 mg/dL. Many different factors create fat in the blood and long-term accumulation, including unhealthy lifestyle, lack of exercise, poor diet, smoking, diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure. high pressure,…
Currently, hyperlipidemia can be classified into two types, based on the cause: primary and secondary.
1. Primary cause
Family history of early coronary disease or stroke: There is a high chance that a person with hyperlipidemia has a male relative (father or brother) under 55 years old or a female relative (mother or sister) under 65 age with coronary heart disease or stroke.
Family history of cholesterol-related condition: Having a parent or sibling with familial hyperlipidemia.
Familial hyperlipidemia is a medical term for high blood fats that run in families and are caused by genetic mutations inherited from parents. People with familial hyperlipidemia have this problem from birth, which can lead to atherosclerosis and early coronary disease.
2. Secondary causes
Lifestyle factors
Unhealthy diet, high in saturated fats such as red meat, cream, butter and other dairy products.
Consuming foods high in trans fats such as popcorn, cookies, chips, carbonated drinks, etc.
Lazy to exercise, sedentary and maintain physical activities.
Using tobacco, drinking a lot of alcohol, alcoholic beverages.
Being overweight and obese.
Health factor
When suffering from these diseases, patients are also at risk for diseases such as: kidney disease, liver disease, hypothyroidism, multiple myeloma, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), primary biliary cirrhosis, chronic kidney disease , diabetes, lupus, sleep apnea.
Symptoms
High cholesterol leads to the accumulation and formation of plaque inside the blood vessels over time, known as atherosclerosis. The longer it is left untreated, the larger the plaque will become, leading to narrowed or blocked blood vessels. People with atherosclerosis face an increased risk of various diseases, depending on which blood vessels are blocked.
1. Coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease, also known as ischemic heart disease or ischemic heart disease, can lead to a heart attack or heart failure. Coronary artery disease is the most common form of heart disease in the United States and the leading cause of death. The coronary artery is the blood vessel that supplies blood to the heart, and when the heart does not receive enough blood due to the obstruction of atherosclerosis, the heart weakens and stops working.
Coronary heart disease can affect even young people. In fact, about one-fifth of people who die from coronary heart disease are under the age of 65. That's why it's so important to get your cholesterol checked at a young age. Because plaque can silently build up in the coronary arteries over time, many young people don't realize it's happening until they develop chest pain (angina) or another sign of a heart attack.
2. Carotid artery disease
The carotid arteries carry blood from the heart to the brain. Carotid artery disease occurs when plaque narrows these arteries so that the brain can't get enough oxygen-rich blood, which can lead to a transient ischemic attack or stroke.
3. Peripheral artery disease
When atherosclerosis affects the arteries in the legs or arms, it is called peripheral artery disease (PAD). The arteries in the legs and arms are called "peripheral" because they are far from the heart and center of the body. PAD is more common in the legs but can also occur in the arms.
PAD is usually asymptomatic and can only be felt when the peripheral artery is at least 60% blocked. The patient has a feeling of pain, fatigue or weakness in the legs, which occurs with movement and decreases with rest (also known as claudication). It is a sign of decreased blood flow due to the growing plaque in the arteries.
PAD can cause serious problems in the legs and feet as well as elsewhere on the body. That's because all blood vessels are connected through the cardiovascular system and so plaque builds up in one area but slows down the entire vascular network.
In the United States, about 1 in 3 adults has high blood pressure, and about 1 in 3 adults has high cholesterol. More than half of the adults in each group had no control over their condition. This means that the treatment is not complete or the person is not using any treatment.
Precautions
1. Scientific, balanced diet
Replace a diet low in saturated and trans fats with a diet high in fiber and unsaturated fats. This can help prevent high cholesterol. Foods like oatmeal, beans, avocados, and vegetable oils can lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol levels.
2. Regular sports activities
Adults should spend time exercising with moderate intensity about 30 minutes / day and at least 5 days / week. You can participate in sports such as running, cycling, swimming, etc.
3. Quit smoking
Quitting or not smoking is one of the main recommendations of the American Heart Association, for the prevention of high cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. After 15 years of not smoking, a former smoker's risk of heart disease is about the same as that of a never-smoker. Smoking damages blood vessels and lowers HDL cholesterol.
4. Limit alcohol intake
Drinking too much alcohol, defined as more than two drinks a day for men and one drink for women, can raise cholesterol and triglyceride levels. A study published in 2020 looking at the effects of alcohol on high blood fats and heart disease, found that alcohol's impact on overall health varied widely, depending on how much and how it was consumed. consume.
5. Maintain a fit body A person with a body mass index (BMI) in the overweight or obese range means that the body is overweight. This slows down the removal of LDL cholesterol from the blood, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke. Therefore, each person should maintain a weight within normal limits, ensuring a BMI between 18.5 - 24.9. Invested in a system of modern machinery such as 4D echocardiogram and vascular machine, 1.5 - 3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging machine, 768-slice MSCT heart and coronary artery, coronary angiography DSA machine system... , Cardiovascular Center of Tam Anh General Hospital receives and treats people with high blood fat and cardiovascular diseases (hypertension, coronary heart disease, valvular heart disease, myocardial ischemia...).





